1/7





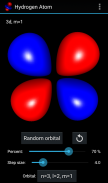


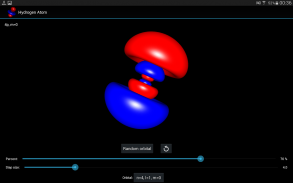

Hydrogen Atom Orbitals
1K+下载次数
567.5kB大小
1.2.1(21-02-2025)最新版本
详情评价版本信息
1/7

Hydrogen Atom Orbitals介绍
氢原子的电子轨道描述原子中电子的波样行为和它们确定的概率找到它在一个特定的空间区域。数学上,轨道是由它的能量本征态的氢原子波函数和本身被确定为解决量子力学薛定谔方程中的波函数来确定。
此应用通过绘制在OpenGL电子概率密度的横截面的表面,并使用移动立方体算法可视化3D中的氢原子的电子轨道。
特征:
- 选择电子轨道通过指定量子数n,l和m来可视化,或者挑随机之一。
- 改变离散化步长。
- 选择总概率找到绘制轨道面内的电子。
- 缩放和旋转轨道与你的手指。
应用程序的源代码是MIT许可下,可在https://github.com/vlvovch/hydrogen-atom-orbitals
Hydrogen Atom Orbitals - APK信息
APK版本: 1.2.1程序包: com.vlvolad.hydrogenatom名称: Hydrogen Atom Orbitals大小: 567.5 kB下载次数: 16版本: 1.2.1发布日期: 2025-02-21 09:15:23最小屏幕: SMALL支持的CPU:
程序包ID: com.vlvolad.hydrogenatomSHA1签名: 7B:93:AA:50:D7:B2:D9:41:45:FB:7F:AF:23:FE:B7:5E:E1:DA:91:2F开发商 (CN): Volodymyr Vovchenko组织 (O): 本地 (L): 国家/地区 (C): UA州/市 (ST): 程序包ID: com.vlvolad.hydrogenatomSHA1签名: 7B:93:AA:50:D7:B2:D9:41:45:FB:7F:AF:23:FE:B7:5E:E1:DA:91:2F开发商 (CN): Volodymyr Vovchenko组织 (O): 本地 (L): 国家/地区 (C): UA州/市 (ST):
Hydrogen Atom Orbitals的最新版本
1.2.1
21/2/202516 下载次数567.5 kB 大小
其他版本
1.2
10/4/202016 下载次数815 kB 大小
1.0.3
13/3/201716 下载次数662 kB 大小

























